Sport nutrition department
Diet and nutrition of football players
Diet plays a key role in the performances improvement of a competitive athlete as well as in the daily sports practice. Energy consumption increases considerably during a fitness activity. That's the reason why the energy balance, the difference between what we consume and the calories we burn, needs an increase in dietary intake.
The increased mobilization of the musculoskeletal system creates multiple injuries in the muscle, bone but also tendon cells. For that purpose, regeneration and new tissue construct are then necessary.
The organism to be able to repair itself and reconstruct at that time will need all the necessary resources in amino acid, lipids and other mineral elements.
If the right nutriments are provided in right quantities at the right time, before, during and after the effort, we can say that the pair sport and diet form the winning combination.
1 / Combine sport and nutrition in order to shape an athletic body and being performant.
In some cases, we can lose weight due to specific life events (stress, illness, tiredness...) or on the contrary gain weight after having been tempted too much by heavy meals, sweets, candies and at the same time having abandoned any fitness activity.
It is then necessary to combine both fitness activity and diet for shaping your silhouette as well as for improving your physical capacities according to your objectives.
Silhouette shaping lies on diet providing caloric intakes and physical activity allowing energy consumption.
The correct energy intake is the one that allows to maintain a weight stable.
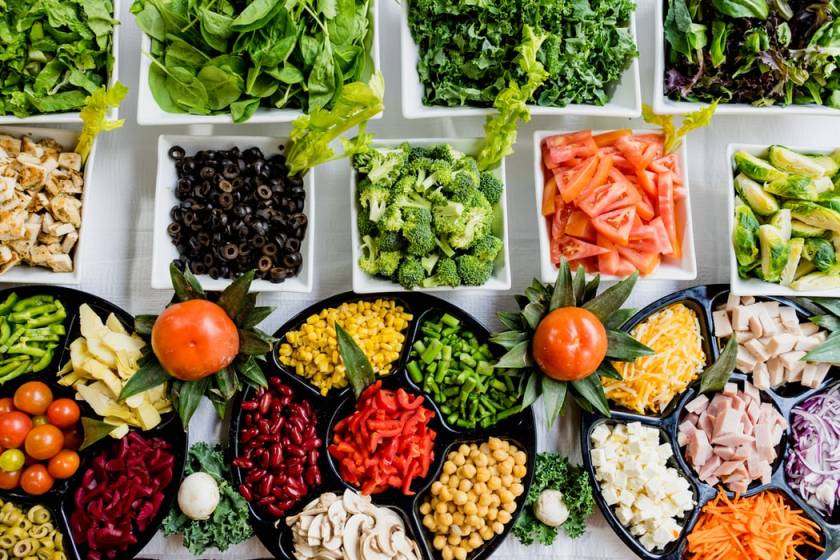

2 / Benefit from an essential diet rebalancing for this high level sports practice
"Whatever the efforts made, we cannot gain weight nor lose weight without a well-balanced diet."
Diet rebalancing consists in adopting a healthy lifestyle that is adapted to its goal or career plan. Indeed, it is meant to last in time unlike the "hard diet" that is temporary.
Eat well does not mean eating anything and no matter how, but regulate daily intakes qualitatively and quantitatively, according to different consumption and needs. The organism needs elements that are necessary for its functioning and its construction, such as : protein, glucides, lipids, as well as vitamins, minerals and fiber.
Quantitatively, we will absorb more calories to gain weight and less to lose weight. In both losing and gaining weight cases, instead of taking a big meal and take some snacks the rest of the day, the key is to split its food intake. Qualitatively, it is important to respect the well-balanced and diversified diet notion that is unfortunately not always followed. It is necessary to consume food that is rich in protein, minerals, fiber and vitamins, but also in sugars and lipids.
Intakes in animal and vegetal protein are used for muscle structure and energy production (meat, shellfish, fish, offal, eggs, charcuterie, dairy products, soya, nuts, hazelnuts, almonds, tofu, legumes...).
Intakes in fiber are recommended for a good intestinal transit (wheat bran, wholemeal bread, white rice, white beans, chickpeas, lentils, peas, artichoke, carrots, potatoes, green cabbage, cauliflower, corn, soya, spinach...), the majority being derived from cereals.
Small amounts of intakes in vitamins are necessary for the organism functioning and come in diverse families (A, B, C, D, E, F...).
Intakes in minerals take the form of ion and are necessary mineral substances in a very small amount for the organism functioning. The main ones are magnesium, iron, calcium and sodium.
Intakes in animal and vegetal lipids that are also called dietary fat provide the human body some fatty acids. That ones are essential because the organism cannot synthesize them and they are a great source of energy for the human body.
Intakes in sugars are the main source of energy. Thus, they are not really essential knowing the organism knows how to create them from other nutriments. Nowadays, lots of food products include sugar.
The main sources of sugars are some cereals, fruits, legumes and some vegetables.
Water requirements :
Sports performance optimization is based on a well-managed hydric balance.
We know that the body contains approximately 65 % of water and that water losses due to perspiration, urine and respiration must absolutely be compensated by at least 1,5 l to 2 l of water intake depending on the climate and level of effort.
In football, it is important to manage properly its hydration level in order to avoid appearance of cramps, tiredness, injuries...
Before a competition, it is useful to have a sufficient and qualitative hydration level, knowing it will depend on several factors : perspiration (more important in warm than cold periods), individual variations between different people and in the same conditions, capacities of the organism in producing and evacuating heat.
During competition, it is important to drink moderately in order to compensate for perspiration.
After competition, it is essential to drink because this is the recovery phase.
An insufficient hydration can create a decrease in performances (2 % of hydration decrease = 20 % of performance decrease) and other risks such as : tiredness, risk of injury, decrease in concentration, increase in reaction time, etc...

3 / Choose to dry muscle or gain muscle mass by developing muscles
What is important for a high level football player is not only the improvement of his body shape but mostly the one of his physical capacities. To reach that point, both caloric intakes and energy consumption have to be considered.
This necessary caloric intake is generated by consumed food while energy consumption are created by the useful activity of the metabolism.
The change in the ratio between needs and energy consumption is done in synergy.
Other parameters are also involved in this balance : quality in the choice of food products, the type of effort, the respect of time slots for food intakes and recovery.
4 / Improve individual physical activity with its personal fitness coach and go out of its comfort zone
Going out of its comfort zone is not an easy thing but is far from being impossible.
Going beyond its limits (the ones we think we reach and overcome) and over time reaching its goals, it helps reboosting one's self-esteem.
That are challenges to go further, step by step. This is hard and painful but with willingness and motivation, we get to it.
With a nice fitness coach and by being full of determination and goodwill, we get to it.
5 / Understand the difference between the terms "food", "nutrition" and "dietetics" as well as their meaning
Food refers to the eating habits as well as the nature of what we eat.
Nutrition teaches us why some food products are essential for our health and other are bad. It also refers to phenomena bringing nutriments to the cells while assuring transformation and good utilization of food to the organism. We are then talking about nutriments.
Dietetics or Science of food hygiene refers to the set of rules to apply to have a well-balanced diet. It explains what to eat and how. We are then talking about food products.
6 / Know the professional football players characteristics and their energy needs
Most players train almost every day and play at least a match per week during the year. Then, to maintain a good performance capacity and avoid chronic tiredness or some injury, it is important to satisfy the right energy needs.
Football is a complex and intermittent sport activity that creates for some players a high energy need due to repetitive and highly intense efforts necessary for great performance. The intensity of this need can vary depending on the player's role within the team.
Sugars stocked in the form of glycogen in muscles and the liver are in principle the source of energy production. Tiredness that comes in the end of a match results from the depleted glycogen reserves in diverse muscle fiber. During competition, the free fatty acids level then increases in the bloodstream during a game in order to compensate the level of muscle glycogen.
Energy needs of a football player are the following :
The necessity of bringing protein is not only restricted to qualitative needs (essential amino acids) but also to quantitative needs (total grams of azote).
7 / Know your food products better according to food groups
| Food products | Contained nutriments | Role for the organism |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy products | Protein, vitamins B, calcium, lipids, vitamins A and D for unalleviated products | Construction and maintenance of muscle structure and transmission of muscle contraction |
| Meat, fish, shellfish, eggs, charcuterie | Protein, iron, vitamins B, B12 and D, more or less lipids | Construction and muscle renewal, transmission of muscle contraction |
| Starch (bread, cereals, rice, pasta, potatoes, couscous, pulses)Sweet products | Glucides, vitamins B, mineral salts | Construction and muscle renewal, transmission of muscle contraction |
| Fruits, green vegetables | Fiber, glucides, vitamin C, mineral salts | Digestive transit, antioxidant capacity |
| Fat | Vitamins A (butter) and E (oils rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids) Essential fatty acids | Energy source, components of the cell membrane |
8 / Understand the notion of daily portion to consume that must be adapted to a professional football player
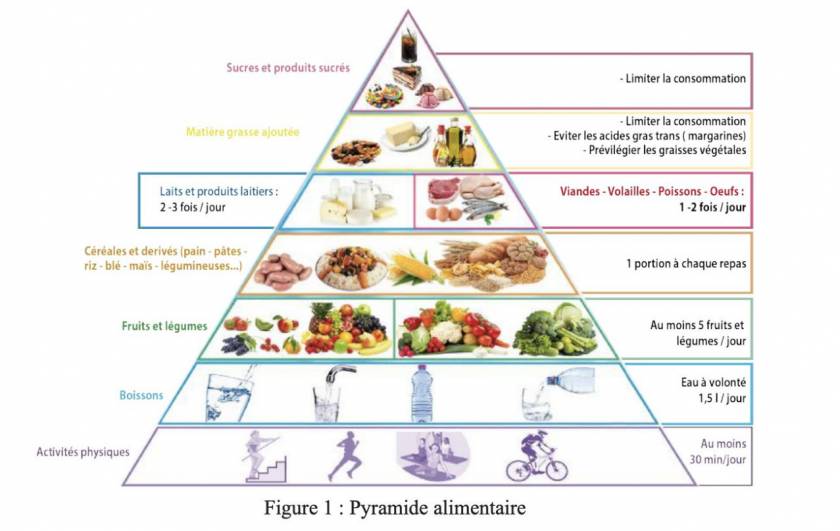
For a high-level athlete, being a football player or practicing another activity, the respect of a diet must be strict. It represents the types of aliments and the number of portions that must be consumed every day.
Below, the recommended serving sizes for each type of product.
The notion of portion :
Vegetable and fruits
Grain products
Milk and substitutes
Meat and substitutes
9 / Know the different nutriments : sugars and their glycemic index, protein and lipids
| High GI (>70) | Moderate GI (between 56 and 69) | Low GI (< 55) |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits | ||
| Dates 103 | Fresh apricots 57 Melon 67 Cherries 63 Papaya 56 Ripe banana 65 |
Fresh apple 38 Dried apricots 30 Grapefruit 25 Grape 53 Not too ripe banana 52 |
| Dried figs 61 Dried grapes 64 Pineapple 59 Apricots in syrup 64 Peaches in syrup 58 |
Kiwi 53 Pear 38 Orange 42 No sugar added apple juice 44 No sugar added grapefruit juice 48 Pure orange juice 50 Tomato juice 38 |
|
| Oleaginous fruits | ||
| Pecan nuts 10 Salty cashew nuts 22 Salty grilled peanuts 14 |
||
| Legumes | ||
| Boiled dried green lentils 48 Red lentils 26 Canned lentils 48 Boiled dried chickpeas 28 Pea 41 |
||
| Soya and derived products | ||
| Calcium enriched soya milk 36 Soya milk and fruits yogurt 50 Tofu (does not contain any sugar) |
||
| Potato | ||
| Baked potato 95 Instant mashed potatoes 83 Boiled peeled potato 78 Boiled unbleached potato 78 Fries 82 |
Steamed unbleached potato 65 | Cooked sweet potato 46 Chips 54 |
| Cereals and derived products | ||
| White french baguette 95 White french baguette (60 g) with chocolate spread (20 g) 72 White sandwich bread 70 Wholemeal sandwich bread 71 White rusk 68 Waffles 76 Apricot Barquette LU 71 Kellogg’s Corn Flakes 77 Kellogg’s Corn pops 80 Kellogg’s Rice Krispies 82 Kellogg’s Smacks 71 Instant oatmeal 82 Puffy rice cake 85 Fast cooking rice 6 min 87 |
Wholemeal bread 65 White french baguette (60 g) with butter (10 g) and raspberry jam (20 g) 62 Croissant 67 Bichoco Prince, BN 56 Traditional oatmeal 59 Kellogg’s Spécial K 56 Boiled white rice 64 Basmati rice 58 Gnocchi 68 Polenta 68 |
Integral bread 49 Pumpernickel (deutsch black bread) 50 Dried biscuit (petit beurre) 50 LU P’tit déjeuner chocolate 42 Kellogg’s All-Bran 34 Natural granola 49 Macaroni 47 Rice sticks 35 Spaghettis cooking 10-15 min 44 Wheat Ebly cooking 10 min 50 Brown rice 50 Supreme pizza Pizza Hut 36 |
| Soda, drinks | ||
| Coca-cola 63 Fanta orange 68 Beer 66 |
||
| Sweets, candies, snacks | ||
| Glucose 100 Candies 78 |
White sugar (saccharose) 68 Mars chocolate bar 68 Milk chocolate 64 Commercial honey 62 Jam 66 |
Fructose 10 Snickers 41 Twix 44 M&M’s 33 Maple syrup 54 No added sugar apricot jam 55 Nutella 33 |
| Dairy products | ||
| Glucose 100 Candies 78 |
Sweetened condensed milk 61 | Low fat fruits yogurt 26 Whole milk 27 Semi-skimmed milk 30 Ice creams 47 |
10 / Know the water needs of professional football players
Thirst is the whistle that alerts the body it misses water. It is then useful to drink regularly in a moderate quantity before being thirsty. Before and during your trainings or matchs, you must drink mineral waters like Hepar or Contrex that are specifically adapted to allow an efficient kidney work. That will allow you to eliminate and reject your metabolic waste.
After a match, it is better to drink rich in bicarbonate and sodium water such as sparkling waters like Vichy Célestin or Badoit. Sodium will come to renew and replace acid present in your organism whereas bicarbonate will come to reject cumulated acidity.
The body is made of approximately 65 % of water. To get back the organism losses (urine, respiration, perspiration, etc...), the daily hydric intake must be equal or greater than 1,5 l. Of course, if you're enduring physical activity, that need will increase.
During a muscular contraction, chemical energy of cellular oxidation produces :
Heat produced by muscles is transferred mainly by evaporation and in a sweat form.
Hydric losses
Hydric losses can go from 0,5 l to 1l/h for an amateur runner, 1,5 l to 2,5l/h for a professional runner and until 3 to 4l/h for a football or tennis match for professionals. A hydric restriction is extremely harmful for performances and the decrease in performance in proportional to dehydration. The feeling of thirst corresponds to a loss of 1 % of your body weight implying that the decrease in performance is already engaged. You then need to drink before being thirsty.
Energy consumption of a football player varies according to the intensity of efforts, the climate and the environment in which the match occurs. During ninety minutes, the player is constantly moving with a varying intensity. During football matches as in every longlasting physical activity, a rise in central temperature due to the rise of the energy metabolism level, creates a water and electrolyte loss by sweating even in a tempered climate.
Dehydration
Dehydration often generates a decrease in performance, risk of injury as well as a bad recovery phase.
In case of dehydration :
Dehydration signs :
11 / Be aware of the possibility to rely on dietary supplements for football players
We mean by dietary supplements, "foodstuff which role is to complete the usual diet and which constitutes a concentrated source of nutriments or other substances having a physiological or nutritional effect alone or combined..." (Directive 2002/46/CE of the European Parliament, transposed by decret n°2006-352 March 26th 2006).
The objective of that complements is to increase the amino acids intake and then "construct" muscle. Every protein food supplement has its own features : casein, whey protein, egg and soya protein or even tri-protein. Each has its own specificities regarding their amino acids content and in their origin. The interest then resides in varying their consumption.

Whey Protein
Coming from milk, it is the favorite protein of bodybuilders. Highly enriched in amino acids and very quickly assimilable by the organism (approximately 30 min), it is then perfectly adapated right after a big workout.
Whey protein or lactoserum, is the most popular protein and it owes its reputation to a very high assimilation speed, a maximal absorption and a very high essential amino acids concentration including BCAA. We use the powder whey in order to optimize all the muscle construction programs, weight gain or loss, but also to improve muscle recovery. Lactoserum is a product derived from milk. Different types of lactoserum actually exist with specific degrees of filtration. Choice is made upon the kind of objective, needs and specificities of each athlete. Whey protein is declined in several degrees of filtration : whey concentration, whey isolate and hydrolysate.
AACR
AACR are essential amino acids present in all animal protein, made of leucine, isoleucine and valine. They must be brought by food because the body does not know how to create them itself. Especially determinant for muscle construction, AACR support anabolism by improving protein synthesis, by reducing muscle tiredness and by struggling efficiently against catabolism. Muscle need AACR before, during and after training in order to improve performances during training as well as to delay the feeling of exhaustion and speed up the muscle recovery process.
Creatine
It is used for ATP re synthesis by increasing the creatine and creatine-phosphate rates inside the muscle. It is naturally absorbed through aliments like fish or red meat. The purpose intended by nutriments is then to "fill up" the muscle in creatine in order to improve muscle contraction during an effort whether it to be brief or intense.
Probiotic
Probiotics are useful micro-organisms that compose the oral, intestinal and vaginal flora. Their presence especially allows to struggle against the proliferation of harmful micro-organisms that could for example provoke infectious diarrhea or vaginits. Probiotics also contribute to the digestion of aliments. More notably, it is admitted that fermented dairy products, like yogurt, ease the lactose digestive process especially for intolerant people. Supplements of some probiotics, like lactobacilles for example, also have that effect but to a lesser extent.
In a healthy organism, the digestive tract is colonized by approximately 100 000 billion of bacteries belonging to 400 different species. 30 to 40 different species of that bacteries represent 99 % of the flora that forms a stable ecosystem being essential for health maintenance. Any event disturbing intestinal flora could provoke diarrhea. That could be an illness (infection, weakened immune system), but also a medical treatment especially in the case of antibiotic.
Spirulina
Biological spirulina, a microscopic alga considered as a "super-food", constitutes a qualitative food supplement knowing it is enriched in assimilable iron and natural protein. 100 % natural and biological, our spirulina contains more beta-carotene, iron, vitamin B12 and gamma-linoleic acid than any other aliment. It is as rich in vitamin E as wheat, but also as rich in calcium, phosphorus and magnesium as milk.

